NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite captured Clear Lake, California, U.S. An algal bloom clouded the waters of California’s Clear Lake in mid-May 2024.
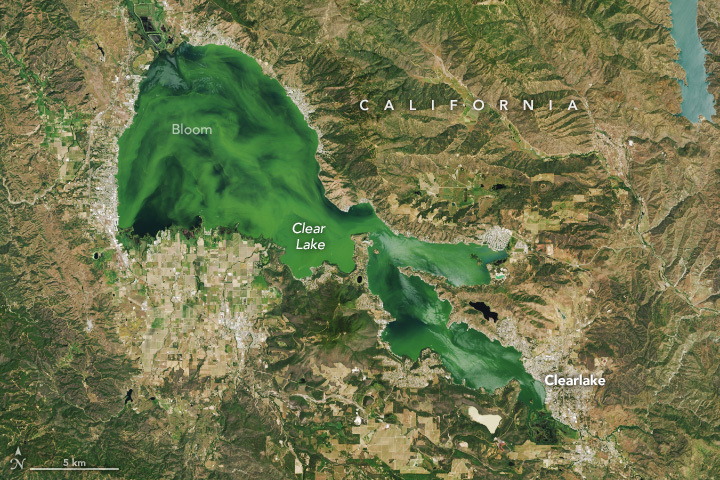
Clearlake, by the lake with the same name, is a city in Lake County at an elevation of 432m. The first inhabitants of Clearlake were the Pomo Indians, who named many of the area’s features, including Mount Konocti. Clear Lake is a naturally nutrient-rich, eutrophic lake that supports the growth of algae and aquatic plants. According to sediment cores, it has long contained large algal populations, possibly since the end of the last ice age about 10,000 years ago. In recent years, however, people have increased nutrient inputs to the lake, and the number of harmful blooms has increased. Nutrients such as phosphorus enter the lake through its tributaries and drive the growth of excess algae. Runoff from nearby farms, vineyards, faulty septic systems, gravel mines, and an abandoned open-pit mercury mine contributes to water quality issues in the lake.
The local scenery on the ground is as follows.

Reference: NASA Earth’s Tweet
See earthview photo gallery: LiVEARTH