NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite captured Macquarie Island.
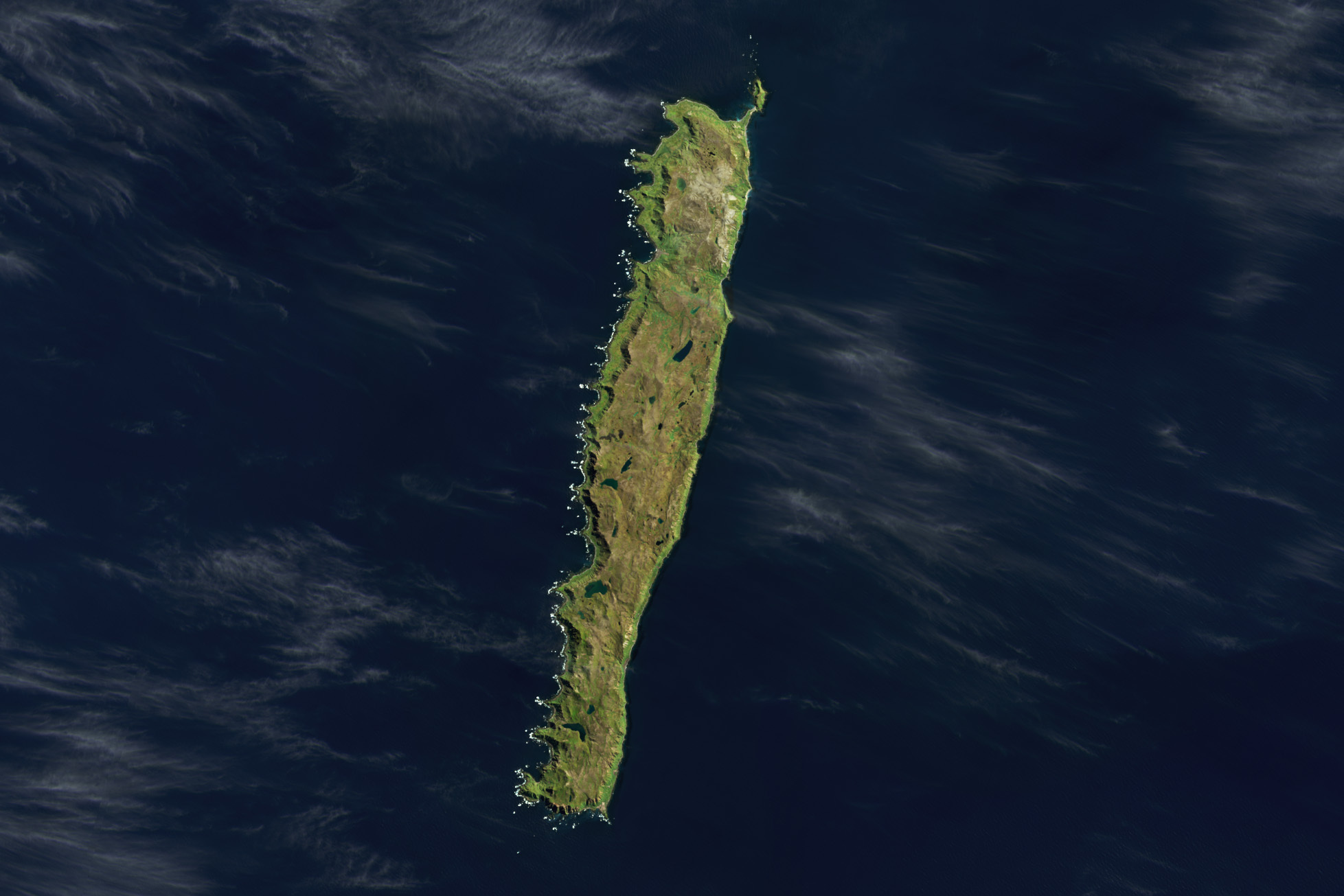
Macquarie Island is an island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. Regionally part of Oceania and politically a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1900, it became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978 and was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997. Macquarie Island is an exposed portion of the Macquarie Ridge and is located where the Australian Plate meets the Pacific Plate. Macquarie Island’s climate is moderated by the sea, and all months have an average temperature above freezing; although snow is common between June and October, and may even occur in summer. Due to its cold summers, the island has a Tundra climate (ET) under the Köppen climate classification. The flora has taxonomic affinities with other subantarctic islands, especially those south of New Zealand.
The local scenery on the ground is as follows.

Reference: NASA Earth’s Tweet
See earthview photo gallery: LiVEARTH